AI FileMaker Lexicon: Essential Glossary for FileMaker Users
Introduction: Why an AI Glossary for FileMaker?
Well, the truth is there’s a lot to learn about AI in FileMaker, and I find myself (similar to AI) enjoying structured output to easily look up definitions, understand and reference concepts. I’ll be the first to admit, the language of AI can be overwhelming, especially for FileMaker users and developers who want to adopt new technologies responsibly. This glossary is designed to boost AI literacy, demystify jargon, and support responsible adoption within the FileMaker ecosystem.
Who Is This For?
This guide is for FileMaker users, developers, and anyone curious about how AI concepts apply to low-code platforms. Whether you’re integrating AI features or just want to understand the buzzwords, this FileMaker AI lexicon is your starting point.
How to Use This Glossary
- Each entry is composed of three parts:
- A clear definition of the term.
- An explanation of how it applies directly in FileMaker.
- A practical example.
- If you’re new to AI, start with the basics. If you’re experienced, use this as a reference for best practices and responsible adoption.
- Since a picture is sometimes worth a thousand words, I’ve included illustrations of terms where appropriate.
Claris Help AI Definitions
I also really like this new feature in the Claris Help. If you search for a term like “RAG,” you get a quick definition pop-up as well as the relevant help articles. So great!
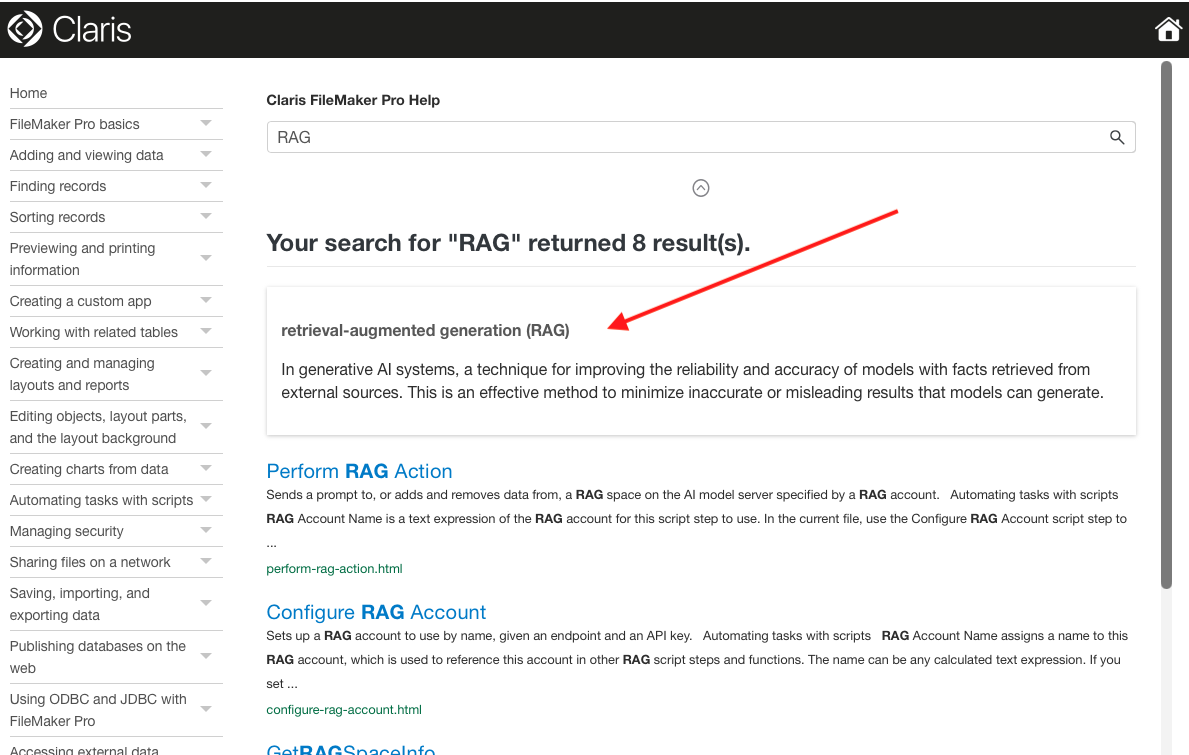
And now, on the the glossary.
AI FileMaker Glossary
AI (Artificial Intelligence)
Definition: A broad field of computer science that enables machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, problem-solving, decision-making, and understanding natural language. The simulation of human intelligence by machines, especially computer systems. Includes learning, reasoning, and self-correction. UiPath’s Ultimate AI Glossary
FileMaker Usage: AI can be integrated into FileMaker workflows to enhance automation, data analysis, and decision-making processes, and is done by integration with various types of AI.
Example: FileMaker solutions integration OpenAI’s GPT-5 model to analyze customer feedback and provide analysis for improved customer service.
AI Agent
Definition: There are various definitions of the term AI Agent, but it is primarily agreed upon that this is an AI integration that contains the ability to reflect upon its responses before delivering them, as well as use preconfigured tools made accessible to the system. It’s also likely a Large Language Model (LLM) to manage workflow execution and decision-making, with the ability to perform tasks independently on a user’s behalf. They have access to various tools to interact with external systems for gathering context and taking actions, always operating within defined guardrails.
FileMaker Usage: AI Agents can be configured to automate tasks, such as updating records or generating reports, by interacting with external APIs through FileMaker scripts.
Example: An AI Agent updates inventory levels in FileMaker by pulling real-time data from a supplier’s API.
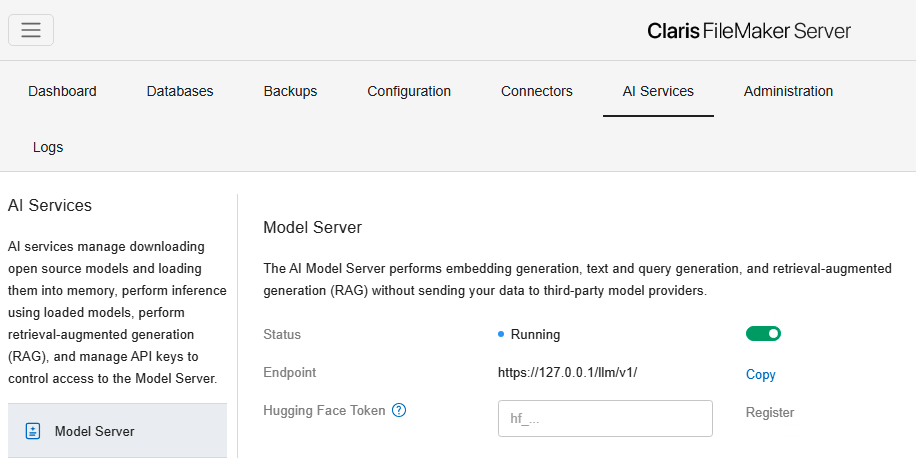
AI Services (FileMaker)
Definition: This is the component that was made available in FileMaker 22 via the FileMaker Server Admin Console, providing capabilities to deploy, configure, and manage AI services locally with security and privacy through the FileMaker Server Admin Console.
FileMaker Usage: AI Services enable organizations to host and manage AI models directly within their FileMaker Server environment for secure and private operations.
Example: A FileMaker Server runs an AI model locally to classify incoming support tickets and assign them to the appropriate team.
Agentic Mode
Definition: An advanced interaction mode in FileMaker’s Generate Response from Model script step where the LLM can request to use external tools you’ve defined, enabling the AI to trigger FileMaker actions to get real-time data or perform operations.
FileMaker Usage: Agentic Mode allows FileMaker solutions to dynamically execute scripts or retrieve external data based on AI-driven decisions.
Example: A FileMaker script uses Agentic Mode to fetch the latest sales data from an external database and generate a performance summary.
Algorithm
Definition: A set of rules or step-by-step instructions that a computer follows to solve a problem or perform a specific task. Algorithms are fundamental to all computer programs and are the basis for AI and machine learning processes (learn more about algorithms).
FileMaker Usage: Algorithms are used in FileMaker scripts, calculations, and custom functions to automate workflows, process data, and implement logic for AI integrations.
Examples:
A FileMaker script uses a sorting algorithm to organize customer records by purchase date before generating a sales report.
Bias (in AI/Data)
Definition: Inherent perspectives or distortions in data that can lead to unfair or inaccurate outcomes when used to train AI models. Every dataset carries a “worldview” shaped by choices made during its creation, which can embed biases.
FileMaker Usage: Bias in data can impact the accuracy and fairness of AI-driven insights in FileMaker solutions, necessitating careful data preparation and validation.
Example: A FileMaker solution trained on biased customer feedback data may incorrectly prioritize certain customer segments over others, leading to skewed business decisions, especially when using predictive models, like the regression model.
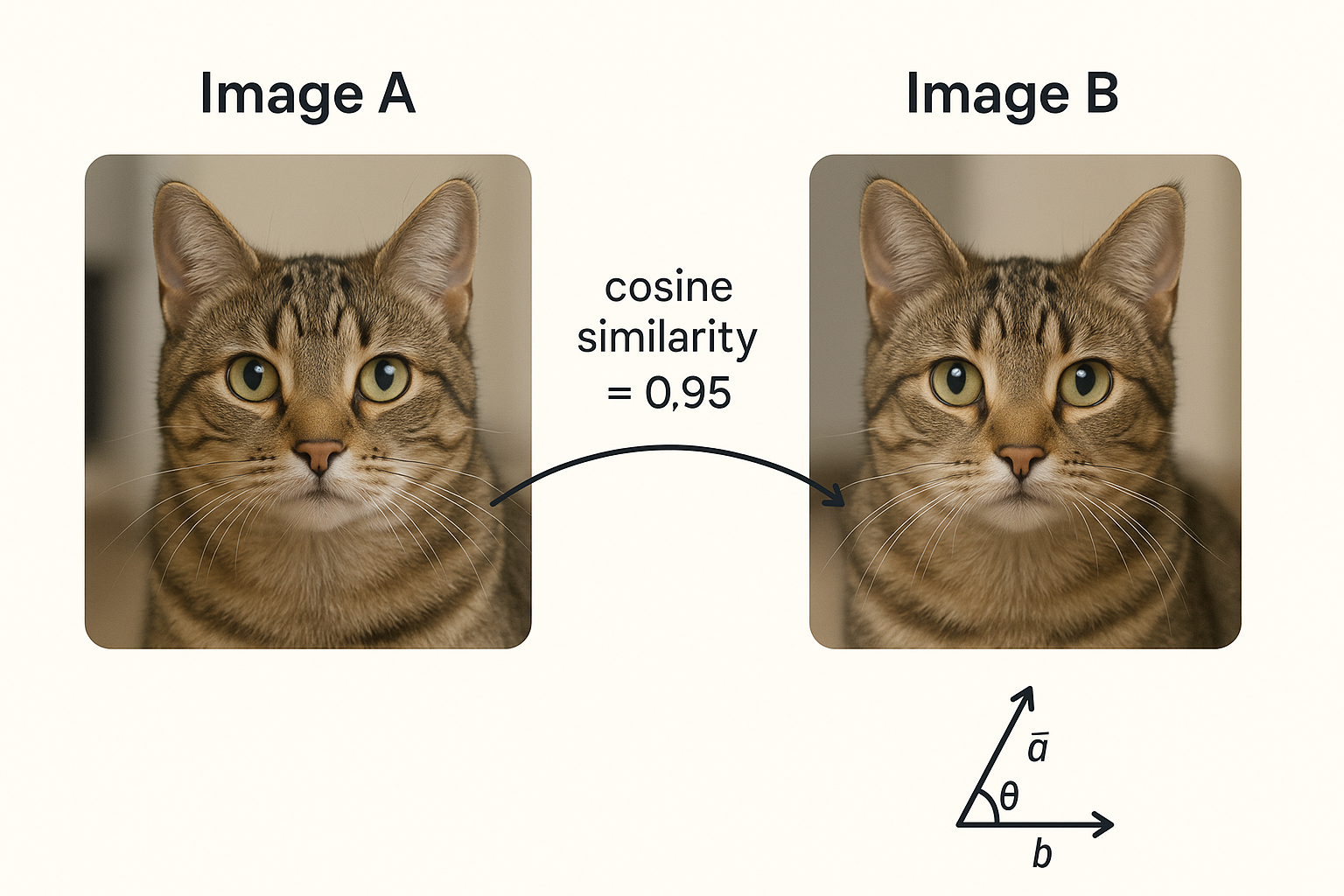
Cosine Similarity
Definition: A method to measure how similar two sets of data (embedding vectors) are by calculating the cosine of the angle between them.
FileMaker Usage: FileMaker uses cosine similarity to compare how closely two pieces of text or data are related, such as finding similar records on a degree varying from 0 to 1.0, where 1.0 is a perfect match.
Example: FileMaker compares a new support ticket to past tickets to find the most similar issues.
Classifier
Definition: A machine learning model that automatically categorizes data into predefined classes, e.g., classifying shapes as “shaded” or “unshaded”. How data is categorized can significantly impact the conclusions about the classifier’s performance and any bias it exhibits.
FileMaker Usage: FileMaker can leverage the CLIP-ViT-B/32 model to classify images by analyzing their semantic content. This allows users to sort and categorize images based on their visual and contextual meaning, enhancing workflows that involve image management or search functionality.
Example: FileMaker uses the CLIP-ViT-B/32 model to classify uploaded product images into categories like “electronics,” “furniture,” or “clothing,” enabling more efficient inventory organization and retrieval.
Context Prompt
Definition: Extra information you give to an AI to help it understand your request better.
FileMaker Usage: Used as a parameter in FileMaker’s Perform Find by Natural Language script step, a context prompt can provide details like today’s date or internal acronyms to improve search accuracy.
Example: Adding “Today’s date is September 10, 2025” as a context prompt helps FileMaker return accurate results for “today’s orders.”
Data Governance
Definition: The overarching framework and processes for managing data, including policies, procedures, and technologies, to ensure data quality, integrity, and compliance.
FileMaker Usage: Data governance in FileMaker involves setting up rules and processes to keep data accurate, secure, and properly used.
Example: FileMaker administrators set permissions and validation rules to ensure only clean, accurate data is entered.
Data Liquidity
Definition: The ability to seamlessly access, combine, and analyze data from various sources. It is considered one of the most important attributes for successful AI deployment, enabling firms to extract relevant information and apply it effectively to specific business scenarios.
FileMaker Usage: FileMaker’s integrations and APIs help users move and use data from different systems easily.
Example: FileMaker pulls sales data from an online store and combines it with in-house inventory records for analysis.
Data Poisoning
Definition: A cyberattack method where data used to train an AI model is intentionally targeted and injected with malicious information
FileMaker Usage: If you use AI models with FileMaker, ensure your training data is secure to prevent tampering.
Example: FileMaker administrators regularly audit training data to detect and remove suspicious entries.
Data Quality
Definition: The accuracy, completeness, and reliability of data.
FileMaker Usage: High-quality data in FileMaker leads to better AI results; clean and accurate records are essential.
Example: FileMaker runs scripts to check for missing or inconsistent data before using it for AI analysis.
Embedding / Vector Embedding
Definition: A numerical representation of data (like text or images) that allows AI systems to compare and analyze meaning. Numerical representations (lists of numbers, vectors) capture the meaning or essence of a piece of data, usually text or images. Data points with similar meanings will have vectors that are closer together in a high-dimensional mathematical space.
FileMaker: Used in FileMaker for semantic find script steps, as well as RAG feature.
Example: FileMaker compares a new support ticket to past tickets to find the most similar issues.
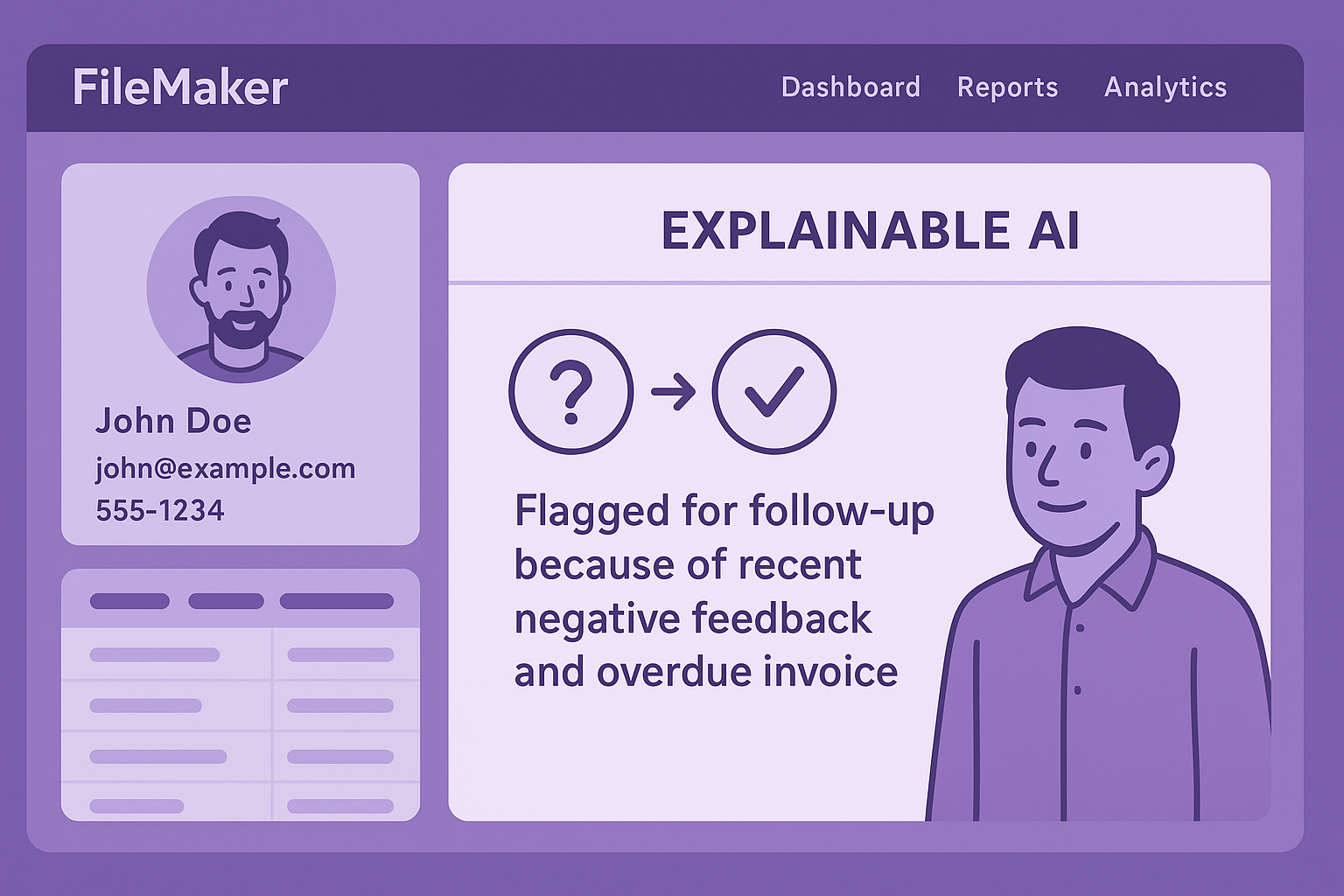
Explainable AI (XAI) / Comprehensible AI (CAI)
Definition: Approaches that aim to provide explanations for AI decisions. This can involve making user interfaces comprehensible to prevent confusion and surprise, and allowing interactive exploration of decision spaces. Wikipedia: Explainable artificial intelligence
FileMaker Usage: These approaches can help make AI-driven features in FileMaker more transparent and user-friendly by offering clear insights into how decisions are made.
Example: A FileMaker solution uses explainable AI to show users why a particular customer was flagged for follow-up, reducing confusion and increasing trust in the system.
Fine-tuning (LLM)
Definition: The process of tailoring an existing Large Language Model (LLM) with custom datasets to make it better for specific business needs, such as understanding company jargon or following particular response styles. FileMaker 2025 supports fine-tuning OpenAI or open-source models using the LoRA algorithm.
FileMaker Usage: Fine-tuning allows FileMaker users to adapt AI models for their organization’s unique terminology, workflows, or compliance requirements, improving the relevance and accuracy of AI-driven features. See the official FileMaker fine-tune model documentation for details on configuring and using fine-tuned models.
Example: An organization exports customer support transcripts from FileMaker, fine-tunes an LLM with this data, and then uses the improved model to generate more accurate automated responses within their FileMaker solution.
GetLiveText (FileMaker Feature)
Definition: A FileMaker function that extracts text from images stored in container fields or from the screen, using Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology.
FileMaker Usage: The GetLiveText function enables users to convert unstructured image data into searchable and actionable text within FileMaker solutions. See the FileMaker documentation for GetLiveText for more details.
Example: A FileMaker solution uses GetLiveText to extract invoice numbers from scanned PDF images uploaded by users, making the data available for automated processing and search.
GetTextFromPDF
Definition: A FileMaker function that extracts text content from PDF files stored in container fields or referenced by file paths. This function enables automated retrieval of readable text from PDF documents for further processing or analysis.
FileMaker Usage: The GetTextFromPDF function allows users to convert unstructured PDF data into searchable and structured text within FileMaker solutions. See the FileMaker documentation for GetTextFromPDF for more details.
Example: A FileMaker script uses GetTextFromPDF to extract contract details from uploaded PDF agreements, enabling automated data entry and compliance checks.
Generative AI
Definition: A type of artificial intelligence that can create new content, such as text, images, or code, rather than just analyzing existing data. Generative AI models are rapidly evolving and are expected to have significant economic and creative impact. Wikipedia: Generative artificial intelligence
FileMaker Usage: Generative AI can be integrated into FileMaker solutions to automatically draft emails, generate reports, summarize documents, or create images based on user input.
Example: A FileMaker script uses a generative AI model to summarize meeting notes and generate action items for the team.
Guardrails
Definition: Well-designed mechanisms to manage risks in AI applications, such as data privacy or reputational risks. Guardrails can be layered and include LLM-based, rules-based (e.g., regex), or moderation API checks. Examples include relevance or safety classifiers, PII (Personally Identifiable Information) filters, and tool safeguards. Wikipedia: Responsible artificial intelligence
FileMaker Usage: Guardrails in FileMaker AI integrations help ensure that AI-driven features operate safely and ethically, such as by filtering out sensitive information or preventing inappropriate content from being generated or displayed.
Example: A FileMaker solution uses a moderation API to scan AI-generated responses for sensitive data before displaying them to users.
Hallucination (AI)
Definition: A risk associated with generative AI where models produce inaccurate or fabricated information that appears plausible. Hallucinations can undermine trust and reliability in AI outputs. Wikipedia: Hallucination (artificial intelligence)
FileMaker Usage: FileMaker solutions that use generative AI should implement safeguards to detect and minimize hallucinations, such as grounding responses in trusted data sources or using retrieval-augmented generation (RAG).
Example: A FileMaker chatbot uses RAG to ensure its answers are based on verified company documents, reducing the risk of hallucinated responses.
Human-in-the-Loop / Human Oversight
Definition: A critical safeguard in AI systems, especially during early deployment, to identify failures, uncover edge cases, and ensure real-world performance without compromising user experience. It involves human intervention, particularly for high-risk actions or when AI exceeds failure thresholds. Wikipedia: Human-in-the-loop
FileMaker Usage: FileMaker solutions can incorporate human oversight by requiring manual review or approval of AI-generated outputs before they are finalized or acted upon, ensuring accuracy and compliance.
Example: An AI-powered FileMaker workflow flags unusual transactions for review, requiring a human administrator to approve or reject them before updating records.

Inference
Definition: The process where a trained AI model makes a prediction or classification based on input data. Inference is the stage where the model applies what it has learned to new, unseen data to generate outputs. Wikipedia: Inference (machine learning)
FileMaker Usage: When calling an external machine learning model via a script (such as using the Generate Response From Model script step), the inference happens when the model call is initiated in that script.
Example: A FileMaker solution sends product descriptions to an AI model and uses the AI Call Logging to view the details of the model inference.
Internal Review Committee (IRC)
Definition: A cross-functional committee responsible for the practical implementation and coordination of Responsible AI efforts, including developing AI policies, tools, and training, and conducting independent reviews of AI projects for technical, ethical, and resource considerations.
FileMaker Usage: Organizations using FileMaker with AI features may establish an IRC to oversee the responsible deployment of AI integrations, ensuring compliance with internal policies and external regulations.
Example: Before launching a new AI-driven automation in FileMaker, the IRC reviews the project to assess risks, data privacy, and alignment with company values.
JSONL (JSON Lines)
Definition: A file format where each line is a valid JSON object, commonly used for preparing training data for fine-tuning large language models. Wikipedia: JSON Lines
FileMaker Usage: FileMaker’s Save Records as JSONL script step allows users to export data in JSONL format, making it easier to prepare datasets for AI training or integration with external machine learning tools.
Example: A FileMaker solution exports customer feedback records as JSONL to create a training dataset for fine-tuning an AI model.
Large Language Model (LLM)
Definition: A type of artificial intelligence capable of understanding and generating human-like text, often by processing vast amounts of data and learning complex language patterns. LLMs can handle complex, multi-step tasks and are foundational to many modern AI applications. Wikipedia: Large language model
FileMaker Usage: FileMaker 2025 integrates LLMs directly into the platform, enabling features like natural language queries, text generation, and advanced data analysis within FileMaker solutions.
Example: A FileMaker script uses an LLM to automatically summarize customer support tickets and suggest responses for agents.
LLM Key (FileMaker Server)
Definition: An API key created and managed by server administrators in the FileMaker Admin Console to control access to specific AI operations (such as embedding generation, text/query generation, fine-tuning, and Retrieval-Augmented Generation). This allows for granular permissions and includes expiration dates for security.
FileMaker Usage: LLM Keys are used to securely manage and restrict which users or scripts can access advanced AI features within FileMaker Server, helping organizations maintain control over sensitive AI operations. See the FileMaker documentation on managing LLM Keys for more details.
Example: An administrator generates a unique LLM Key for the marketing team, allowing them to use AI-powered summarization features in FileMaker while restricting access for other departments.
LLM Tag (FileMaker)
Definition: A special tag [LLM] that can be added to the comments field of fields and tables in the Manage Database dialog. When using features like Perform SQL Query by Natural Language, this tag helps specify relevant fields and tables to the LLM, reducing noise, improving response quality, and enabling data minimization for security.
FileMaker Usage: By tagging fields and tables with [LLM], FileMaker users can guide AI models to focus only on pertinent data, enhancing both performance and privacy. See the FileMaker documentation on using LLM tags for more information.
Example: A developer adds the [LLM] tag to sensitive fields in a customer database, ensuring that only those fields are considered when running natural language queries with AI.
Machine Learning
Definition: A subset of artificial intelligence where systems learn from data to improve performance over time without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning algorithms identify patterns and make predictions or decisions based on input data. Wikipedia: Machine learning
FileMaker Usage: FileMaker can integrate with external machine learning models via APIs, enabling features like predictive analytics, classification, and automated decision-making within FileMaker solutions.
Example: A FileMaker solution sends sales data to an external machine learning model, which predicts future sales trends and returns the results for visualization in FileMaker.
Model (Machine Learning)
Definition: A trained algorithm used to recognize patterns, classify inputs, or generate outputs based on data. Popular models include Open AI’s GPT-5, Anthropic’s Claude 4.5, and Google Gemini 2.5. Models have a variety of ways to be grouped, such as size, function, open source/closed, and are a key component to any AI system. and can be used for tasks such as prediction, classification, and generation. Wikipedia: Machine learning
FileMaker Usage: FileMaker allows for integration with a variety of AI models, both a select set of closed models and also open source models, sending and receiving data from external AI models via APIs for inference, classification, or prediction tasks.
Example: A FileMaker script sends product descriptions to an external AI model (such as OpenAI GPT 4o), receives category predictions, and stores the results in the database.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Definition: A branch of artificial intelligence that enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. NLP combines computational linguistics with machine learning and deep learning models to process text and speech data. Wikipedia: Natural language processing
FileMaker Usage: FileMaker solutions can leverage NLP-powered AI services to analyze customer feedback, extract key information from documents, or enable natural language queries within the database.
Example: A FileMaker script uses an NLP service to extract action items from meeting notes entered as free text.
Natural Language Query (FileMaker)
Definition: A feature in FileMaker 2025 (e.g., Perform SQL Query by Natural Language, Perform Find by Natural Language) that allows users to ask questions or perform searches in plain English. An AI model then converts these queries into structured SQL or FileMaker find requests against the database.
FileMaker Usage: Natural Language Query enables users to interact with FileMaker databases more intuitively, reducing the need for technical query knowledge. See the FileMaker documentation on Perform SQL Query by Natural Languageand Perform Find by Natural Language for more details.
Example: A user types “Show all invoices from last month” into a FileMaker interface, and the system automatically retrieves the relevant records using an AI-powered natural language query.
Open-Source Models
Definition: AI models whose source code, architecture, and training data (in some cases) are made publicly available for use, modification, and distribution. Open-source models foster collaboration, transparency, and innovation in the AI community.
FileMaker Usage: Open-source models can be integrated into FileMaker solutions to provide customizable AI functionalities without relying on proprietary systems. They are particularly useful for organizations that require more control over their AI implementations or need to comply with specific privacy and security standards.
Example: A FileMaker solution integrates the open-source GPT-NeoX model to generate custom reports, allowing the organization to fine-tune the model for internal terminology and workflows.
Prompt Engineering
Definition: The process of designing and refining the prompts given to an AI model to achieve a desired output. Effective prompt engineering helps guide AI models to produce more accurate, relevant, and useful responses. Wikipedia: Prompt engineering
FileMaker Usage: FileMaker’s Configure Prompt Template script step allows users to create reusable templates with constants, making it easier to structure and optimize prompts for AI integrations.
Example: A FileMaker developer creates a prompt template that is optimized to generate clear summaries of meeting notes, improving the quality of AI-generated content across the organization.
Prompt Injection Attack
Definition: A cybersecurity threat where malicious prompts are crafted to elicit unintended responses from a large language model (LLM), aiming to manipulate its behavior, achieve unauthorized access, or bypass security measures. Wikipedia: Prompt injection
FileMaker Usage: FileMaker solutions that integrate with LLMs should validate and sanitize user input to prevent prompt injection attacks, ensuring that AI-driven features remain secure and reliable.
Example: A FileMaker chatbot checks user-submitted prompts for suspicious patterns before sending them to an LLM, reducing the risk of prompt injection exploits.
Regression Model
Definition: An AI model trained to predict numerical values based on input data, such as embedding vectors from text or other data. Regression models are widely used for forecasting, trend analysis, and quantitative predictions. Wikipedia: Regression analysis
FileMaker Usage: FileMaker’s Configure Regression Model script step allows users to train, save, load, and unload regression models for tasks like sales forecasting or risk assessment.
Example: A FileMaker solution uses a regression model to predict monthly sales based on historical transaction data and marketing spend.
Responsible AI (RAI)
Definition: An approach to developing and deploying AI systems in a manner that is ethical, safe, fair, transparent, and accountable. Responsible AI practices include establishing governance structures, ensuring data quality, managing risks, and incorporating human oversight. Wikipedia: Responsible artificial intelligence
FileMaker Usage: Organizations using AI features in FileMaker can adopt Responsible AI principles by implementing data governance, transparency, and human-in-the-loop review processes to ensure ethical and compliant use of AI.
Example: Before deploying an AI-powered automation in FileMaker, the team documents its intended use, reviews for potential bias, and sets up regular audits to monitor outcomes.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Definition: A machine learning approach that combines information retrieval with text generation. RAG improves the quality, relevance, and factual accuracy of AI-generated responses by grounding them in information retrieved from a specific, trusted external knowledge source (such as internal documents). Wikipedia: Retrieval-augmented generation
FileMaker Usage: In FileMaker, RAG involves creating “RAG spaces” for your documents and then sending prompts to these spaces, ensuring that AI-generated answers are based on up-to-date and verified company knowledge. See the FileMaker documentation on RAG for more details.
Example: A FileMaker chatbot uses RAG to answer employee questions by retrieving and summarizing information from the company’s HR policy documents.
RAG Space
Definition: A unique name for a specific knowledge base or collection of documents that you group together within FileMaker’s Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) implementation. RAG Spaces allow compartmentalization of knowledge, so queries can target specific sets of documents (e.g., “HR policies” or “product specs”).
FileMaker Usage: FileMaker users can create and manage RAG Spaces to organize internal documentation and ensure that AI-powered queries are grounded in the most relevant and trusted sources. See the FileMaker documentation on creating RAG Spaces for more information.
Example: The IT department creates a “Security Policies” RAG Space in FileMaker, so that AI-powered helpdesk queries only reference approved security documentation.
Semantic Search
Definition: A method that finds information based on the meaning or context of the query, rather than just matching keywords. Semantic search uses embeddings to understand relationships and relevance, enabling more accurate and intuitive search results. Wikipedia: Semantic search
FileMaker Usage: FileMaker 2025 introduces server-side semantic find functionality, where semantic search operations are executed on the FileMaker Server—even when the search target field is a related field. See the FileMaker documentation on Perform Semantic Find for more details.
Example: A user enters “recent customer complaints about billing” in FileMaker, and the semantic search feature retrieves relevant support tickets even if the exact keywords aren’t present.
SQL (Structured Query Language)
Definition: A domain-specific language used in programming and designed for managing data held in a relational database management system. SQL enables users to query, update, and manage structured data efficiently. Wikipedia: SQL
FileMaker Usage: FileMaker’s Perform SQL Query by Natural Language feature allows AI to generate and execute SQL queries, making it easier for users to interact with their data using plain English.
Example: A user asks FileMaker, “List all customers who made purchases last quarter,” and the system translates this into an SQL query to retrieve the relevant records.
Top-K
Definition: In the context of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), “Top-K” refers to the “top N” or “top k” most relevant document chunks (based on cosine similarity to the user’s query) that are retrieved and sent to the language model for summarization and final answer generation. The value of K determines how many results are considered. Wikipedia: k-nearest neighbors algorithm
FileMaker Usage: The FileMaker Admin Console AI Services setting allows you to configure the “Number of Top Ranked results for RAG summarization,” controlling how many document chunks are retrieved and summarized by the AI.
Example: An administrator sets the Top-K value to 5, so FileMaker’s RAG feature always summarizes the five most relevant policy documents when answering HR questions.
Structured Data
Definition: Data organized into defined fields and formats—such as rows, columns, and schemas—that are easy to query and analyze. Structured data is highly organized and typically stored in relational databases. Wikipedia: Structured data
FileMaker Usage: Most FileMaker tables and fields are considered structured data. For example, a “Clients” table with fields like FirstName, LastName, and Email is structured data, making it suitable for reporting, exporting to APIs, and feeding into AI models for inference.
Example: A FileMaker database stores customer information in structured tables, enabling efficient searches, reporting, and integration with external analytics tools.
Unstructured Data
Definition: Information that lacks a predefined format or organization, making it harder to query or automate. Unstructured data includes text documents, images, audio, video, and other formats that do not fit neatly into tables or schemas. Wikipedia: Unstructured data
FileMaker Usage: In FileMaker, unstructured data can include container fields with images, raw notes in a text field, or imported PDFs. These often require AI or manual processing to become useful for analysis or automation.
Example: A FileMaker solution uses OCR (Optical Character Recognition) to extract text from scanned PDF invoices stored in container fields, converting unstructured data into structured records for reporting.
More AI Literacy Resources
- Financial Times AI Glossary
- UiPath’s Ultimate AI Glossary
- Upwork’s AI Terms Glossary
- Accenture’s Artificial Intelligence Glossary
- Automate.org AI Glossary
Final Thoughts for Now
Understanding AI terms is the first step toward responsible, confident adoption in FileMaker. For more on how to use these concepts in your own solutions, explore the linked resources or reach out to Violet Beacon for a strategy session.
What terms in FileMaker AI are you interested in learning more about?